Setting Up and Invoicing Sales Prepayments in Business Central: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Alfredo Iorio
- Apr 7, 2023
- 6 min read
Effectively managing sales prepayments is crucial for businesses seeking to optimize cash flow and maintain healthy customer relationships. Microsoft Dynamics Business Central, a comprehensive ERP solution, offers robust features that simplify the process of setting up and invoicing sales prepayments. In this step-by-step guide, we will explore the ins and outs of managing sales prepayments within Business Central, empowering you to streamline your operations, enhance financial visibility, and drive business success.

From configuring the general ledger to creating sales prepayment invoices, this guide covers everything you need to know about sales prepayments in Microsoft Dynamics Business Central.
Introduction: Importance of Sales Prepayments
In today's fast-paced business environment, managing cash flow is crucial for any organization's success. Sales prepayment, also known as advance payment or down payment, is an essential tool that can help businesses maintain a steady cash flow by requiring customers to pay a percentage of the total invoice amount upfront. This not only helps businesses avoid financial difficulties but also ensures that they have the necessary funds to cover the costs of fulfilling orders and delivering products or services. Sales prepayments also provide a sense of security and trust between businesses and their customers, as both parties know that their financial commitments are fulfilled.
Benefits of using Microsoft Dynamics Business Central for Sales Prepayments
Microsoft Dynamics Business Central is a powerful business management solution that offers a range of features and functionalities to help businesses streamline their operations and improve their financial management. One of its notable features is its capability to manage sales prepayments seamlessly. By using Business Central, businesses can create and track prepayment invoices, allocate prepayments to specific sales orders, and manage any prepayment-related credits and refunds.
Business Central also provides real-time visibility into cash flow and outstanding prepayment balances, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and take necessary actions promptly. Overall, using Business Central for sales prepayments can help businesses improve their financial performance, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Definition of sales prepayment
A Sales Prepayment is a receipt of cash for a customer order before products or services are delivered. Companies using simple accounting software typically manage sales prepayments as journals to debit a cash account and credit a sales prepayment nominal ledger; afterwards, a user must reverse this transaction when the tax invoice is raised. This simple method works for small organizations; however, larger companies must account for prepayment in their company books while maintaining the link between the accounting side of the prepayment and the customer service side of this process. Therefore, they need a comprehensive solution to manage all the process steps in one place.
A typical sales prepayment process in an ERP is made of the following steps:
Creation of a sales document.
Creation of the request for payment, also called a pro-forma invoice or a prepayment invoice.
Collection and payment allocation.
Invoice the sales document.
Let's look at how the process works in Business Central.
Prerequisites for Setting Up Sales Prepayments
Some initial setup is required to process prepayments in Business Central; if you never used this functionality, it is unlikely that the initial configuration included the necessary setup.
Configuring the number series for prepayments
As I explained before, sales prepayments are transactions that are registered (posted in Business Central) as invoices. Therefore, we need to assign number series before we can use the functionality. The most common setup is to assign the posted sales invoices number series to sales prepayments, and the posted credit memos to the prepayment credit memos.

Setting Up Customer Prepayments Accounts
Before we can register sales prepayments in Business Central, we must setup a sales prepayment nominal ledger in the chart of accounts. For most companies, sales prepayments are considered a liability. Once the goods or services have been delivered, the liability is cancelled and the funds are instead recorded as revenue. The reversal of the prepayment from the liability into revenues is handled automatically in Business Central.

However, some companies - mainly in professional services - register sales prepayments as prepaid revenues in their income statement. Business Central supports both scenarios, as you can see in the picture below where I have set up an income statement account as a sales prepayment for service transactions.

Applying Prepayment Percentages to Items, Customers or Sales Documents
The final setup element to handle sales prepayment is to define prepayment percentages. The most used method to handle prepayments percentages in Business Central is to define a default prepayment percentage on customers or on items.

While the first scenario is the most common, sometimes a default prepayment for customers of items might not be required. For example, when a customer with standard payment terms places an order that exceeds their credit limit. Here, users can define a prepayment percentage on the order.

In the picture above, I have an example of a sales order with a 100% prepayment percentage and dedicated prepayment terms and discount.
Creating Sales Orders with Prepayments
With the proper setup in place, we can go through the entire process to create and post a Sales Prepayment in Business Central. In this example, we will start with an open sales order. For more details on how to create a sales order in Business Central, check my other post here: Mastering Order to Cash Processes: A Comprehensive Guide for IT Managers & CIOs
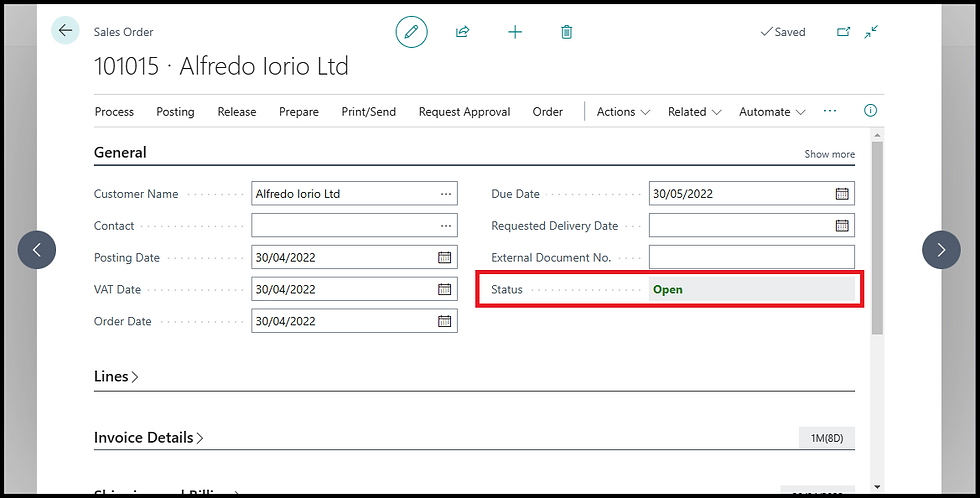
Posting the Sales Prepayment Invoice
The next step is to post the prepayment invoice. The action is under the Prepayment tab on the sales order page. Users can also preview how the entries will post to the general ledger using the function Preview Prepayment Invoice Posting.

Business Central creates a link between the prepayment invoice and the order, which allows the automatic reversal of entries when users register the payment and post the final invoice. As a further help and to avoid double entries, the order status changes from Open to Pending Prepayment

Payment registration and application to the prepayment invoice.
When the customer payment is received, users can register the payment and manage the application. In Business Central, a prepayment invoice shows in the customer ledger entries (customer sub-ledgers) like a normal sales invoice, but with an identifier that helps users find the correct document for the application.

Fulfilling the Order and Posting the Final Sales Invoice
The last step of the process is where users can fulfil the order. In Business Central, the link between the prepayment invoice and the order is always maintained, therefore, users can now release the order and proceed with the fulfilment. For more details on how to ship items, check my other post here: The Complete Guide on how to Ship Items.

Understanding the accounting side of sales prepayments in Business Central
So far, we covered the process of setting up and process sales prepayments; now, we will deep dive into the accounting side of a sales prepayment.
Prepayment invoice: General Ledgers and Customer Sub-ledgers Entries
In Business Central, a prepayment invoice is like a normal sales invoice with one fundamental difference: the amount is registered in a prepayment account. As I mentioned before, this can be a liability in the balance sheet or revenues in the income statement. Regardless of the setup, posting a prepayment invoice in Business Central will result it the following transactions:
Dr. Accounts Receivables
Cr. Prepayment
Cr. Vat

Likewise, the customer sub-ledgers (Customer Ledger Entries in Business Central) show the prepayment invoice as a prepayment document with the original amount.

Cash receipt and allocation: Customer and Bank sub-ledgers
A simple transaction between Cash and AR accounts occurs when users receive cash and apply the receipt to the prepayment:
Dr. Cash
Cr. Accounts Receivables
At the same time, Business Central closes the prepayment invoice and we can see that the prepayment invoice is fully paid because the field Remaining Amount is zero.

Business Central also creates an entry in the bank sub-ledgers (Bank Ledger Entries). This entry will remain Open until a user processes a Bank Reconciliation. More about Bank Rec in a following post.
Sales invoice: Prepayment Reversal in the General Ledger and Customer Sub-ledgers
The last accounting side of a sales prepayment process is the posting of the final invoice. In this phase we have additional entries than in a normal sales invoice where we debit revenues and credit accounts receivables transaction. The entries are:
Dr. Prepayment
Cr. Revenues
The customer ledger entry generated by the sales invoice is already closed because Business Central will automatically apply the prepayment to the new invoice. In the example below, I have an invoice for an item generated from a prepayment. You can see that the prepayment shows on the invoice as an additional line.

Closing Thoughts
Managing sales prepayments is an essential aspect of any business operation that cannot be overlooked. By requiring customers to pay a percentage of the total invoice amount upfront, businesses can maintain a steady cash flow, reduce financial risks, and enhance customer trust. Business Central offers a comprehensive solution for managing sales prepayments that includes the ability to setup default prepayment percentages for customers or individual lines.
Regards
Alfredo Iorio.
Comments